The Fusion Industry Application Research Center at the Energy Research Institute of Hefei Comprehensive National Science Center has recently made significant strides in the technology of multi-pulse repetitive operation for compact torus core fueling. This breakthrough utilizes a pulsed power supply system activated by a spark gap switch, achieving multi-pulse repetitive operation of the compact torus device. In recent platform experiments, a series of ten compact torus plasmas were successfully generated continuously at a repetition rate of 2 Hz. The research outcomes have been documented in the esteemed journal "Fusion Engineering and Design" under the title "Design and operation of a repetitive compact torus injector for the EAST tokamak".
In the context of nuclear fusion reactor operations, maintaining and increasing plasma density necessitates an effective method for injecting fuel particles into the reactor. Direct injection of fuel particles into the reactor core is key to achieving tritium self-sufficiency and high burn rates. The compact torus injection technology is currently seen as an extremely promising approach to core fueling in large-scale tokamak nuclear fusion reactors of the future. A compact torus is a self-organized plasma blob with high density and speed, magnetically confined by its own magnetic field, capable of penetrating strong magnetic fields to reach and fuel the core of a nuclear fusion reactor.
Given the pulsed nature of compact torus formation and acceleration, continuous operation is not feasible, thus making multi-pulse repetitive operation essential for efficient fueling and density maintenance. The enhanced pulsed power supply system integrates high-power pulsed technology with a high-precision timing control system, allowing for multiple spark gap triggers via thyristors to achieve the multi-pulse repetitive operation of the compact torus device. This set of compact torus devices is projected to be installed on the EAST tokamak for fueling experimental research, potentially advancing engineering research on core fueling for future steady-state nuclear fusion reactors.
Dr. Tan Mingsheng from the Fusion Industry Application Research Center is the primary author of the publication, with corresponding authors Researcher Kong Defeng and Associate Researcher Ye Yang. The collaborative team includes members from the Institute of Plasma Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei Proton Leap Technology Co., Ltd., Hefei University of Technology, and Hengyang Normal University. This research has been supported by independent projects from the Energy Research Institute of Hefei Comprehensive National Science Center, collaborative innovation projects from Anhui universities, grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and key research and development projects from Anhui Province.
论文链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fusengdes.2024.114559
For further details, please refer to the publication at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fusengdes.2024.114559
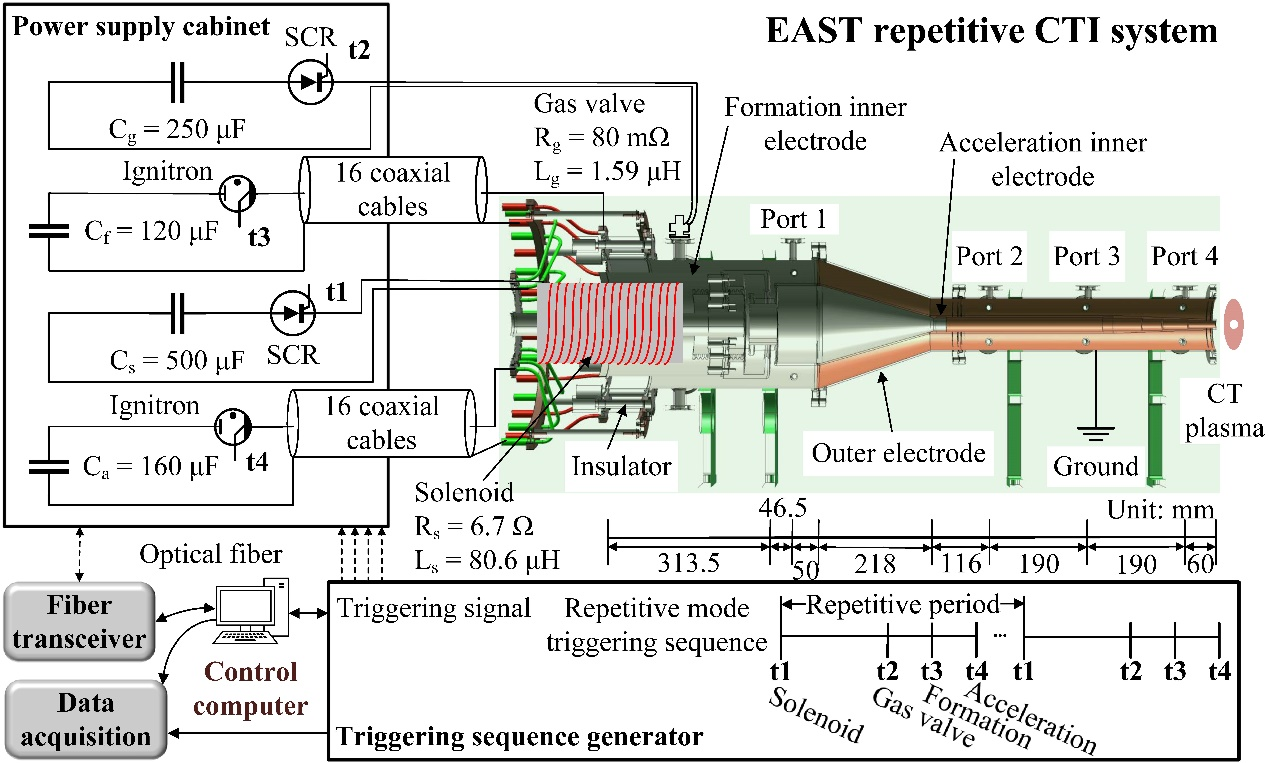
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of the EAST multi-pulse repetitive operation compact torus system: compact torus injector, pulsed power supply system, control system, data acquisition, and various diagnostic devices
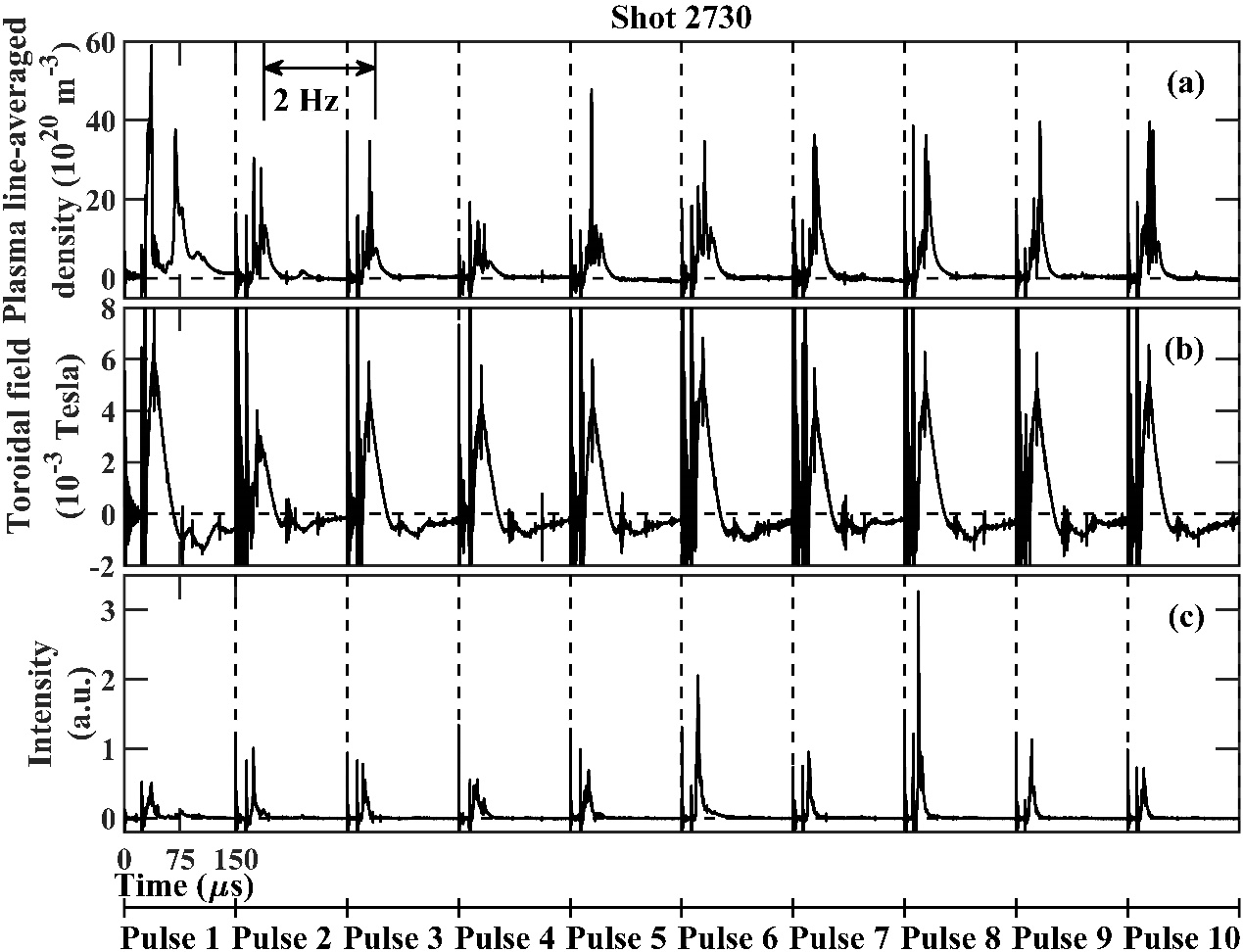
Figure 2: Chord-averaged density, boundary magnetic field, and radiation light intensity of compact torus plasma in repetitive operation mode


